In the realm of pharmacology, certain substances hold the power to intrigue and confound in equal measure. Ketamine, with its complex pharmacological profile and multifaceted effects, stands as a prime example. Often associated with its use as an anesthetic or a recreational drug, ketamine’s raw potential extends far beyond its stereotypical depictions. In this exploration, we delve into the depths of ketamine’s raw form, uncovering its diverse applications, therapeutic promise, and ongoing research endeavors.

Unveiling Ketamine’s Raw Composition
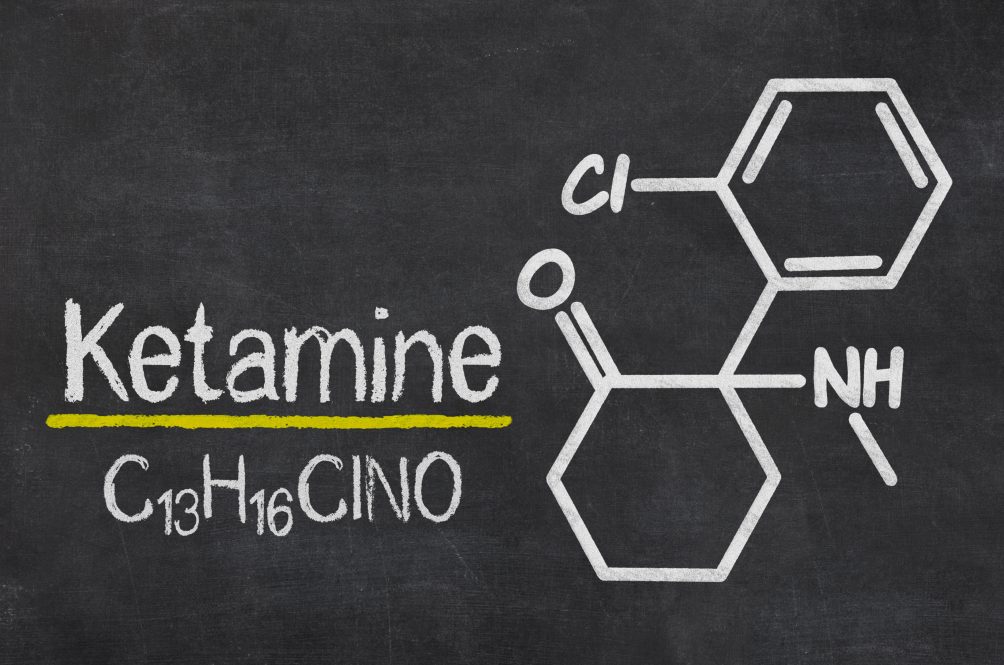
At its core, ketamine belongs to the class of dissociative anesthetics, altering perception and inducing a state of detachment from reality. Chemically known as (RS)-2-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-(methylamino)cyclohexanone, ketamine’s molecular structure embodies a delicate balance between its dissociative and analgesic properties. In its raw, crystalline form, ketamine appears as a fine powder, soluble in water and possessing a characteristic bitter taste.
The synthesis of ketamine typically involves the reaction of cyclohexanone with a mixture of bromine and methylamine, followed by purification processes to obtain the desired product. This raw material serves as the foundation for various pharmaceutical formulations, ranging from injectable solutions for anesthesia to intranasal sprays for the treatment of depression.
The Anesthetic Legacy
Since its discovery in the 1960s by Dr. Calvin Stevens, ketamine has revolutionized the field of anesthesia, offering rapid onset and short duration of action compared to traditional agents. As a raw ingredient in anesthesia, ketamine continues to play a pivotal role in surgical procedures, particularly in resource-limited settings where access to sophisticated equipment may be limited.
Beyond its use in traditional anesthesia, ketamine’s unique pharmacological profile has found applications in procedural sedation, particularly in emergency departments and outpatient settings. Its ability to provide analgesia and amnesia while preserving airway reflexes makes it a versatile tool for healthcare providers across various specialties.

The Gateway to Mental Health
In recent years, ketamine has garnered significant attention for its potential as a breakthrough therapy in the realm of mental health. Emerging research has highlighted its rapid and robust antidepressant effects, challenging conventional treatment paradigms for conditions such as treatment-resistant depression (TRD) and bipolar disorder.
As a raw material in the development of novel therapeutics, ketamine has paved the way for the synthesis of next-generation antidepressants targeting the glutamatergic system. Intravenous ketamine infusion and intranasal esketamine, the S-enantiomer of ketamine, have gained regulatory approval for the treatment of depression, offering hope to millions of individuals grappling with the debilitating effects of mood disorders.
Navigating the Neurochemical Landscape
Central to ketamine’s therapeutic actions is its interaction with the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, a key player in synaptic plasticity and glutamatergic neurotransmission. By blocking NMDA receptors and enhancing synaptic connectivity, ketamine triggers a cascade of neurobiological changes, including the release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and restoration of synaptic homeostasis.
Moreover, ketamine’s modulation of other neurotransmitter systems, such as serotonin, dopamine, and GABA, contributes to its complex array of effects on mood, cognition, and perception. The intricacies of ketamine’s neurochemical actions continue to be elucidated through preclinical and clinical studies, offering insights into its therapeutic potential across a spectrum of psychiatric disorders.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its promise, ketamine therapy is not without its challenges and considerations. Concerns regarding abuse potential, dissociative side effects, and long-term safety remain subjects of ongoing debate and research. Furthermore, the accessibility and affordability of ketamine-based treatments pose barriers to widespread adoption, particularly in underserved communities.
Ethical dilemmas surrounding off-label use and the commodification of ketamine therapy underscore the need for responsible prescribing practices and comprehensive patient monitoring. As research advances and clinical guidelines evolve, addressing these challenges will be paramount in maximizing the benefits of ketamine while minimizing potential harms.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Ketamine
As we stand at the precipice of a new era in mental health care, ketamine’s raw potential beckons us to explore uncharted territories and challenge conventional wisdom. From the operating room to the psychiatrist’s office, ketamine’s journey from raw material to therapeutic agent symbolizes the enduring spirit of innovation and discovery in medicine.
Moving forward, harnessing ketamine’s full potential will require interdisciplinary collaboration, rigorous scientific inquiry, and a steadfast commitment to patient-centered care. By embracing curiosity and cultivating compassion, we can unlock the enigma of ketamine and usher in a new era of hope and healing for generations to come.


